728x90
이번에 뭘 다뤄야 하나 생각하다가
opencv document를 보니
이번에는 이미지 그라디언트를 볼 차래더라
이미지 그라디언트는 이미지의 기울기를 구하는 것을 말한다.
이 기울기는 영상내 급격히 변하는 곳으로 영상 내 물체의 윤곽선(에지)가 된다.
이에 대한 설명은 다음 링크와 cmu 슬라이드에서 잘 설명해주고 있다.
ref
www.cs.cmu.edu/~16385/s17/Slides/4.0_Image_Gradients_and_Gradient_Filtering.pdf
그러면 이미지 그라디언트 코드를 구현해보자.
우선 소벨 필터를 이용한 이미지 그라디언트
"""
ref
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edge_detection
- http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~16385/s17/Slides/4.0_Image_Gradients_and_Gradient_Filtering.pdf
- https://iskim3068.tistory.com/49
"""
def sobel_kerenl():
kernel_x = np.array([
[-1, 0, 1],
[-2, 0, 2],
[-1, 0, 1]
])
kernel_y = np.array([
[1, 2, 1],
[0, 0, 0],
[-1, -2, -1]
])
return kernel_x, kernel_y
def sobel(img, method=None):
"""
get image gradient using sobel operater
parameteres
------------
img : input image applying sobel filter
method : 1(x direction), 2(y dicrection), 3(x + y direction)
"""
k_size = 3
rows, cols = img.shape
kernel_x, kernel_y = sobel_kerenl()
pad_img = padding(img, k_size=k_size)
res_img = np.zeros((rows,cols))
sx, sy = 0, 0
for i in range(0, rows):
for j in range(0, cols):
boundary = pad_img[i:i+k_size, j:j+k_size]
if method == 1:
sx = np.sum(kernel_x * boundary)
elif method == 2:
sy = np.sum(kernel_y * boundary)
else:
sx = np.sum(kernel_x * boundary)
sy = np.sum(kernel_y * boundary)
res_img[i,j] = np.sqrt(sx**2 + sy**2)
return res_img
x 방향, y 방향, x+y방향 영상 시각화 결과
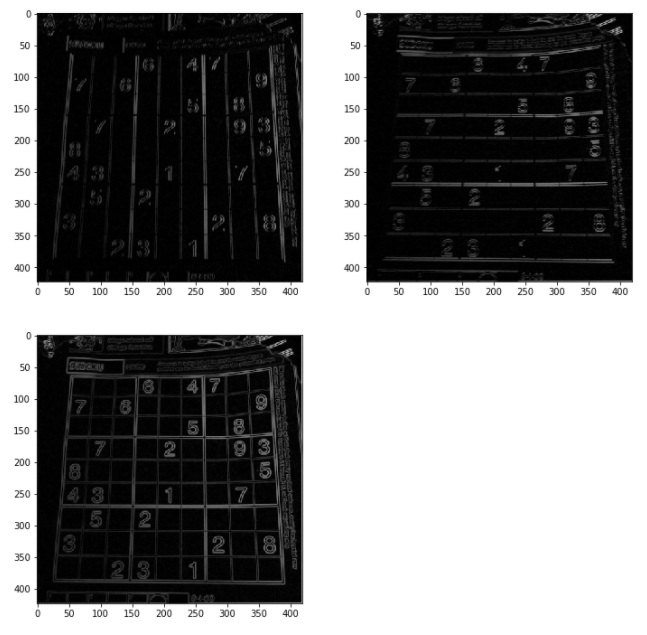
plt.figure(figsize=(12,12))
for i in range(1, 4):
plt.subplot(2, 2, i)
sobel_img = sobel(img, method=i)
plt.imshow(sobel_img,cmap="gray")
라플라시안 그라디언트 영상

def laplacian_filter():
kernel_x = np.array([
[0, 1, 0],
[1, -4, 1],
[0, 1, 0]
])
kernel_y = np.array([
[0, -1, 0],
[-1, 4, -1],
[0, -1, 0]
])
return kernel_x, kernel_y
def laplacian(img):
"""
get image gradient using laplacian filter
parameteres
------------
img : input image applying laplacian filter
"""
k_size = 3
rows, cols = img.shape
kernel_x, kernel_y = laplacian_filter()
pad_img = padding(img, k_size=k_size)
res_img = np.zeros((rows,cols))
sx, sy = 0, 0
for i in range(0, rows):
for j in range(0, cols):
boundary = pad_img[i:i+k_size, j:j+k_size]
sx = np.sum(kernel_x * boundary)
sy = np.sum(kernel_y * boundary)
res_img[i,j] = np.sqrt(sx**2 + sy**2)
return res_img
laplacian_img = laplacian(img)
plt.imshow(laplacian_img,cmap="gray")
300x250
'로봇 > 영상' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 컴퓨터 비전 알고리즘 구현 - 11. 허프 변환 (0) | 2020.12.03 |
|---|---|
| 컴퓨터 비전 알고리즘 구현 - 10. 캐니 에지 검출기 만들기 (0) | 2020.12.01 |
| 컴퓨터 비전 알고리즘 구현 - 8. 모폴로지 연산 (0) | 2020.11.30 |
| 컴퓨터 비전 알고리즘 구현 - 7. 가우시안 스무딩 (0) | 2020.11.30 |
| 컴퓨터 비전 알고리즘 구현 - 6. 평균 스무딩 (0) | 2020.11.30 |